Introduction
Chess is one of the world’s oldest and most enduring games. It’s admired for its deep strategy, elegant simplicity, and universal appeal. If you’ve ever wondered where did chess originate, you’re not alone. It’s a cultural touchstone, a mental sport, and a symbol of intellect across the globe.
But where did chess originate?
The story of chess is as rich and layered as the game itself. When asking where did chess originate, we find that it spans empires, languages, and centuries of human innovation. From ancient battlefields to royal courts, chess has evolved through cultural exchanges and historical shifts to become the modern game we recognize today.
In this blog, we’ll take a journey through time to uncover the origins of chess – beginning in ancient India and tracing its path through Persia, the Arab world, and medieval Europe – revealing how each civilization shaped the game into what it is now.

Where Did Chess Originate? Ancient Beginnings in India
Exploring where chess originated takes us to India around the 6th or 7th century CE. This ancient game was called chaturanga, a Sanskrit word meaning “four divisions”, referring to the four branches of the Indian military: infantry, cavalry, elephants, and chariots.
Chaturanga pieces symbolized military units: pawns (infantry), knights (cavalry), bishops (elephants), and rooks (chariots). Ashtāpada, an 8×8 grid, predated modern boards and influenced today’s chess layout.
Chaturanga introduced pieces with unique moves and the key goal of protecting the king.
This innovative combination of strategy and symbolism marked the beginning of chess as a game of both warfare and intellect.
Refinement in Persia: Shatranj
The story of where chess originated continues in Persia, where the game was refined into shatranj. This adaptation retained the core structure of the Indian game but introduced new rules and strategic depth that brought it closer to the chess we know today.
One of Persia’s most lasting contributions to chess was the introduction of terminology still used today. Persians introduced terms like “shah” for king, leading to today’s “check.” The phrase shah mat, meaning “the king is helpless,” evolved into the modern term checkmate.
Shatranj was more than entertainment. Tt taught tactics, foresight, and risk management. The game was esteemed in Persian culture and art.
Chess in the Arab World
After conquering Persia, Arabs adopted shatranj, spreading it in the Islamic world. Chess spread widely, integrating Arabic language and culture.
Arabic influence refined chess terminology and documentation. While many Persian terms remained, the Arabic language shaped how the game was taught, played, and documented. Arab scholars documented shatranj strategies, preserving the game’s legacy.
Chess spread via trade, inspiring variants like xiangqi in China and shogi in Japan – games that share strategic elements with chess while reflecting local traditions and aesthetics.
Chess became a respected intellectual pursuit, evolving as it reached Europe.
European Transformation
Chess entered Europe through Islamic connections, notably via Spain and Italy. By the 12th and 13th centuries, shatranj was well established in European society – but it didn’t stay static for long.
Beginning around 1200 CE, Europeans began experimenting with the rules, leading to transformative changes in how the game was played. These modifications breathed new life into chess and set it on the path to becoming the dynamic, high-paced battle of minds we know today.
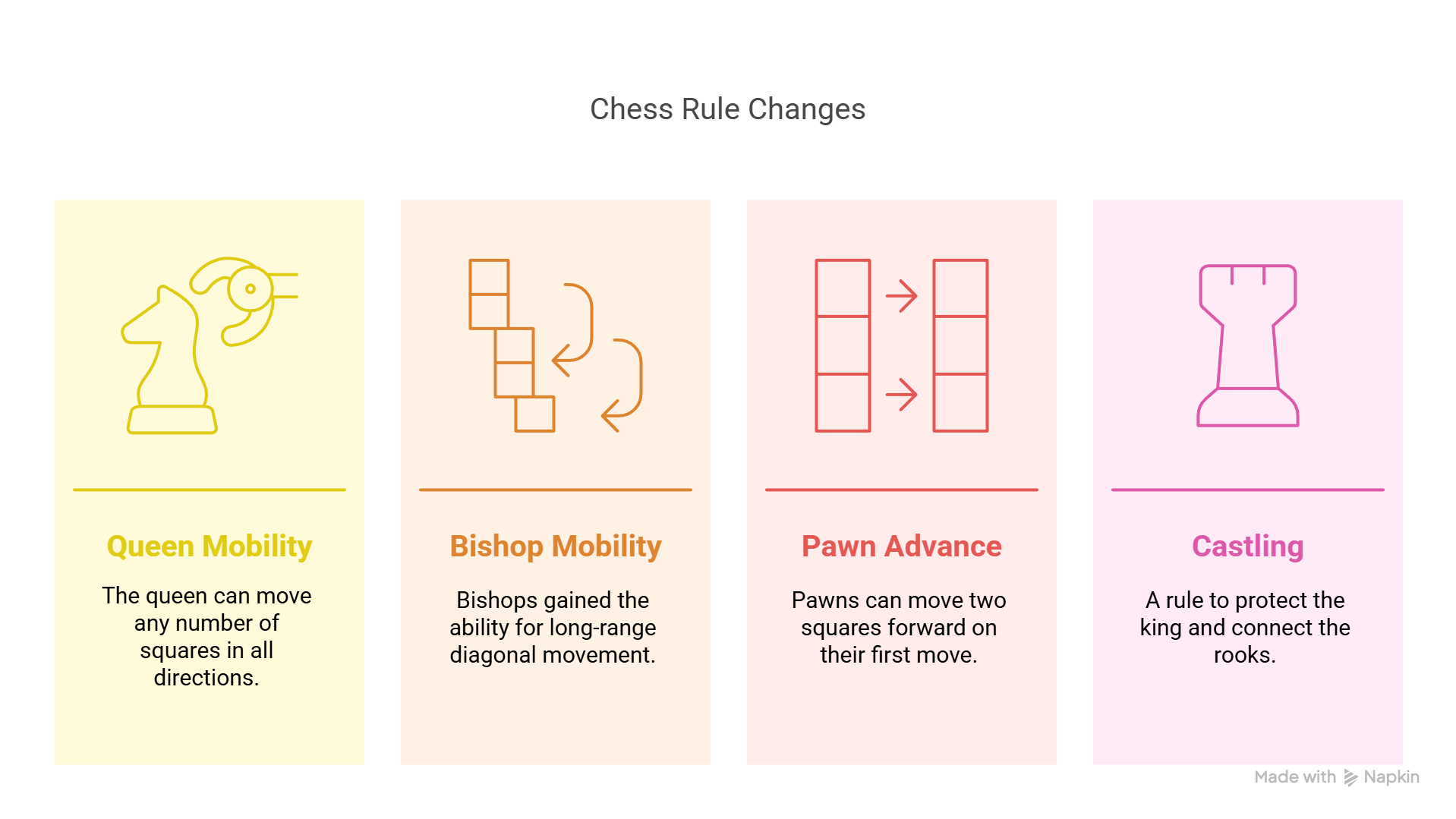
Key innovations included:
- Queen and bishop mobility: The queen, once a relatively weak piece, was empowered to move any number of squares in all directions. Bishops gained long-range diagonal movement. These changes made the game far more tactical and fluid.
- Two-square pawn advance: Pawns were now allowed to move two squares forward on their first move, speeding up development and opening play.
- Castling: This rule was introduced to protect the king and connect the rooks, adding a vital layer of defensive strategy.
Innovations accelerated chess, broadening its appeal and strategic depth. The transformation marked the birth of what we now recognize as modern chess.
Modern Chess: The Standard Game Emerges
By the late 15th century, these rules formed the standard global version of chess.. Modern chess quickly became popular across Europe – in royal courts, universities, and coffee houses.
Chess’s popularity led to the inaugural World Championship in 1886.
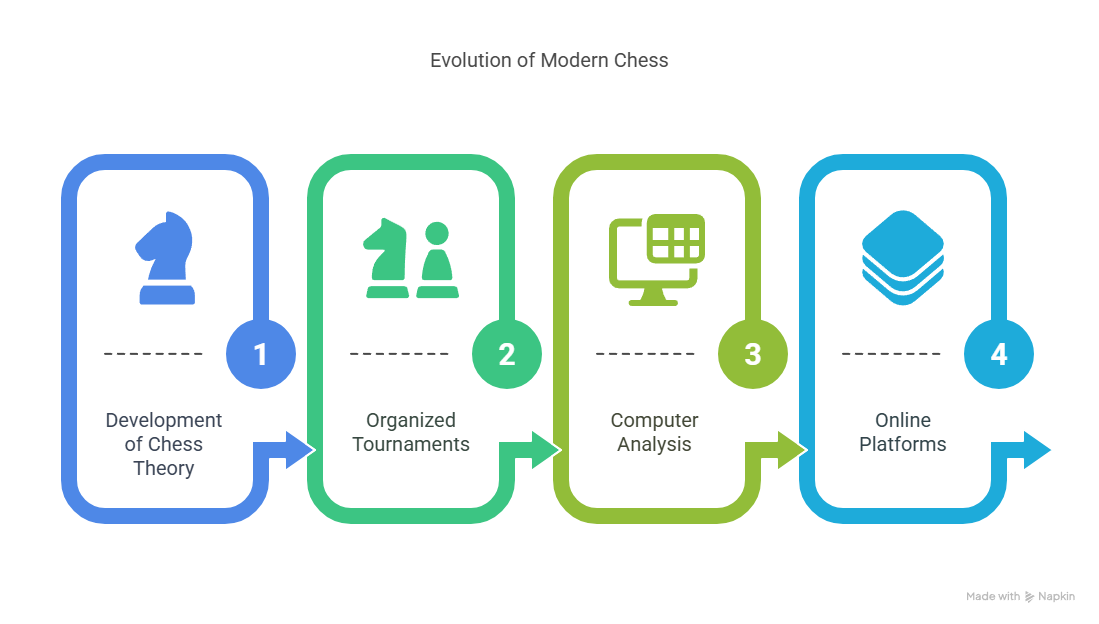
Over the following centuries, chess continued to evolve in parallel with human progress. Some major advancements include:
- Chess theory: A vast body of opening principles, middlegame strategies, and endgame techniques began to take shape, deepening the intellectual complexity of the game.
- Organized tournaments: National and international events created a thriving competitive scene.
- Computer analysis: With the advent of computers, players gained tools to analyze games with incredible precision.
Online platforms: Digital platforms globalized chess, enabling widespread access and play.
Modern chess is a global sport, educational tool, and cultural bridge inspiring all ages.
If you want to improve your overall play, take a look at my post on How to Get Better at Chess.
Where Did Chess Originate? Final Thoughts
So, where did chess originate? From its earliest roots in India as chaturanga, through its refinement in Persia as shatranj, adoption and expansion in the Arab world, and eventual transformation in Europe, the story of chess is one of remarkable evolution shaped by centuries of cultural exchange.
Each civilization that embraced the game added its own flavor – refining rules, redefining strategy, and enhancing its appeal. Chess evolved into a symbol of creativity and shared intellectual pursuit.
Today, chess stands as a timeless symbol of strategy and intellect, transcending language and geography. Its journey through history continues to inspire, reminding us that great ideas evolve – and endure.
If you’re curious about the history or want to elevate your chess skills, don’t hesitate to contact us with any questions you may have or lessons tailored to your needs.
FAQ
1. Where did chess originally come from?
Chess began in 6th–7th century India. Chaturanga represented military divisions and led to modern chess.
2. How did chess spread to other parts of the world?
Chess moved from India to Persia, then through the Islamic world to Europe – mainly via Spain and Italy.
3. What were the major changes to chess when it reached Europe?
In medieval Europe, key rule changes transformed chess into its modern form. These included increased mobility for the queen and bishop, the two-square pawn advance, and the introduction of castling – all of which made the game faster and more dynamic.
4. When did modern chess as we know it become standardized?
By the late 15th century, the new rules had solidified into a standardized version of the game. The first official World Chess Championship was held in 1886.
5. Has chess continued to evolve in recent times?
Yes! The game has advanced through organized tournaments, the rise of chess theory, computer-assisted analysis, and online platforms that allow people worldwide to learn and play. Chess today is more global and accessible than ever.
